For Windows 7, 8 and 10, Windows Server 2010 you can use the built-in Resource Monitor for this.
- Open Resource Monitor, which can be found
- By searching for resmon.exe in the start menu, or
- As a button on the Performance tab in your Task Manager
- Use the search field in the Associated Handles section on the CPU tab
- Pointed at by blue arrow in screen shot below
In case it is not obvious, when you have found the handle, you can identify the process by looking at the Image and/or "PID" column.
You can then end the application if you are able to do that, or just right-click the row and you'll get the option of killing the process right there.

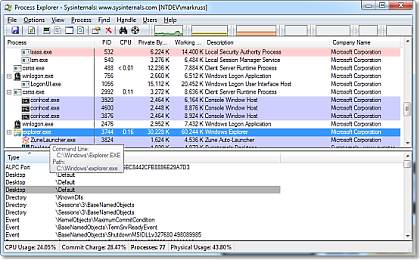
Additionaly in Windows XP, you can use Microsoft/SysInternals Process Explorer - Go to Find > Find Handle or DLL. In the "Handle or DLL substring:" text box, type the path to the file (e.g. "C:\path\to\file.txt") and click "Search". All processes which have an open handle to that file should be listed.
"The Process Explorer display consists of two sub-windows. The top window always shows a list of the currently active processes, including the names of their owning accounts, whereas the information displayed in the bottom window depends on the mode that Process Explorer is in: if it is in handle mode you'll see the handles that the process selected in the top window has opened; if Process Explorer is in DLL mode you'll see the DLLs and memory-mapped files that the process has loaded. Process Exploreralso has a powerful search capability that will quickly show you which processes have particular handles opened or DLLs loaded.
The unique capabilities of Process Explorer make it useful for tracking down DLL-version problems or handle leaks, and provide insight into the way Windows and applications work. " From docs.microsoft.com

No comments:
Post a Comment